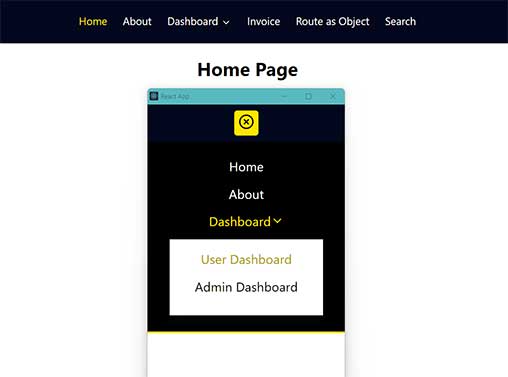
Creating a responsive navbar using ReactJS involves breaking down the task into smaller steps. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you create a basic responsive navbar using React:
Set Up React App:
If you haven't already, create a new React app using Create React App or your preferred method.
npx create-react-app react-router-v6
cd react-router-v6
npm install react-router-dom@6
npm start
Run the following commands:
A browser window will open http://localhost:3000/
Next, Project structure your folder as follows.
src
├── components
| ├── Nav.css
| ├── Nav.js
├── page
| ├── About.js
| ├── AdminDashboard.js
| ├── Home.js
| ├── Invoice.js
| ├── OrderDetails.js
| ├── Orders.js
| ├── RouteAsObj.js
| ├── Search.js
| ├── Style.css
| ├── UserDashboard.js
| ├── UserEditProfile.js
| └── UserProfile.js
├── App.css
├── App.js
├── index.css
└── index.js
1. Index File (index.js):
index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import './index.css';
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(
<browserrouter> <app> </app></browserrouter>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
This file initializes the React application, wraps it with BrowserRouter to enable routing, and renders the App component at the root element.
2. App Component (App.js):
App.js
import { Route, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import Nav from "./components/Nav";
import Home from "./page/Home";
import About from "./page/About";
import Invoice from "./page/Invoice";
import RouteAsObj from "./page/RouteAsObj";
import Search from "./page/Search";
import UserDashboard from "./page/UserDashboard";
import UserProfile from "./page/UserProfile";
import UserEditProfile from "./page/UserEditProfile";
import AdminDashboard from "./page/AdminDashboard";
function App() {
return (
<div className='app'>
<Nav />
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
{/* Approach #1 */}
<Route path="/user">
<Route index element={<UserDashboard />} />
<Route path="profile" element={<UserProfile />} />
<Route path=":editId" element={<UserEditProfile />} />
<Route path="admin" element={<AdminDashboard />} />
</Route>
{/* Approach #2 */}
<Route path="invoice/*" element={<Invoice />} />
<Route path="object_route/*" element={<RouteAsObj />} />
<Route path="search" element={<Search />} />
<Route path="*" element={<NotFound />} />
</Routes>
</div>
);
}
export const NotFound = () => {
return <div><h1> 404 page not found </h1> </div>
}
export default App;
This component serves as the main structure of the application, defining routes using the react-router-dom library. It includes navigation, home, about, user, invoice, object_route, search, and a not-found page.
3. Navigation Component (components/Nav.js):
components/Nav.js
import { NavLink, Outlet } from "react-router-dom";
import React,{useState} from 'react';
import {FiAlignRight,FiXCircle,FiChevronDown } from "react-icons/fi";
import "./Nav.css";
const Nav = () => {
const [isMenu, setisMenu] = useState(false);
const [isResponsiveclose, setResponsiveclose] = useState(false);
const toggleClass = () => {
setisMenu(isMenu === false ? true : false);
setResponsiveclose(isResponsiveclose === false ? true : false);
};
let boxClass = ["nav__container"];
if(isMenu) {
boxClass.push('responsive__nav__show');
}else{
boxClass.push('');
}
const [isMenuSubMenu, setMenuSubMenu] = useState(false);
const toggleSubmenu = () => {
setMenuSubMenu(isMenuSubMenu === false ? true : false);
};
let boxClassSubMenu = ["sub__menus"];
if(isMenuSubMenu) {
boxClassSubMenu.push('sub__menus__Active');
}else {
boxClassSubMenu.push('');
}
return (
<div className='nav'>
{isResponsiveclose === true ? <>
<span className="menubar__button" style={{ display: 'none' }} onClick={toggleClass} > <FiXCircle /> </span>
</> : <>
<span className="menubar__button" style={{ display: 'none' }} onClick={toggleClass} > <FiAlignRight /> </span>
</>}
<ul className={boxClass.join(' ')} >
{/* Approach #1 --- Active */}
<li><NavLink onClick={toggleClass} className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="/">Home</NavLink></li>
{/* Approach #2 --- Active */}
<li>
<NavLink onClick={toggleClass} style={({ isActive }) => {
return {
color: isActive ? "#ffe500" : ""
};
}} to="/about">About</NavLink>
</li>
<li onClick={toggleSubmenu} className="sub__menus__arrows"><NavLink className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="/user">Dashboard <FiChevronDown /> </NavLink>
<ul className={boxClassSubMenu.join(' ')} >
<li><NavLink onClick={toggleClass} className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="/user">User Dashboard</NavLink></li>
<li><NavLink onClick={toggleClass} className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="/user/admin">Admin Dashboard</NavLink></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li><NavLink onClick={toggleClass} className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="/invoice">Invoice</NavLink></li>
<li><NavLink onClick={toggleClass} className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="/object_route"> Route as Object </NavLink></li>
<li><NavLink onClick={toggleClass} className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="/search"> Search </NavLink></li>
<Outlet />
</ul>
</div>
);
};
export default Nav;
page/Invoice.js
import React from "react"
import {NavLink, Routes, Route, Outlet } from "react-router-dom"
import Orders from "./Orders";
import OrderDetails from "./OrderDetails";
import "./Style.css";
const Invoice = () => {
return (
<div className='admin__dashboard'>
<h1> Invoice </h1>
<ul>
<li> <NavLink className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="profile">Profile</NavLink> </li>
<li> <NavLink className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="orders">Orders</NavLink> </li>
<li> <NavLink className={({ isActive }) => isActive ? "active" : ""} to="review">Review</NavLink> </li>
</ul>
<div className="dashboard">
<Routes>
<Route path="profile" element={<Profile />}></Route>
<Route path="orders" element={<Orders />}></Route>
<Route path="review" element={<Review />}></Route>
<Route path="order_details/:orderId" element={<OrderDetails />} />
</Routes>
</div>
<Outlet />
</div>
)
}
export const Profile = () => {
return <h2>Profile</h2>
}
export const Review = () => {
return <h2>Review</h2>
}
export default Invoice
page/RouteAsObj.js
import React from "react"
import { useRoutes, Outlet } from "react-router"
import { Link } from "react-router-dom"
const RouteAsObj = () => {
let element = useRoutes([
{ path: "/", element: <Route1 /> },
{ path: "route2", element: <Route2 /> },
{ path: "route3",element: <Route3 />,
// children can be used to configure nested routes
children: [
{ path: "child1", element: <Child1 /> },
{ path: "child2", element: <Child2 /> },
],
},
{ path: "*", element: <NotFound /> },
])
return (
<div className='admin__dashboard'>
<ul>
<li> <Link to="">Route1</Link> </li>
<li> <Link to="route2">Route2</Link> </li>
<li> <Link to="route3">Route3</Link></li>
</ul>
{element}
</div>
)
}
const Route1 = () => <h1>Route1</h1>
const Route2 = () => <h1>Route2</h1>
const Route3 = () => {
return (
<div>
<h1>Route3</h1>
<ul>
<li> <Link to="child1">Child1</Link> </li>
<li> <Link to="child2">Child2</Link> </li>
</ul>
<Outlet />
</div>
)
}
const Child1 = () => <h2>Child1</h2>
const Child2 = () => <h2>Child2</h2>
const NotFound = () => <h1>NotFound</h1>
export default RouteAsObj
page/Search.js
import React, { useRef } from "react"
import { useLocation, useNavigate } from "react-router-dom"
function useQuery() {
// Use the URLSearchParams API to extract the query parameters
// useLocation().search will have the query parameters eg: ?term=bar&a=b
return new URLSearchParams(useLocation().search)
}
const Search = () => {
const query = useQuery()
const term = query.get("term")
const inputRef = useRef(null)
const navigate = useNavigate()
const formSubmitHandler = e => {
//prevent the default form submission
e.preventDefault()
//extract search term using refs.
const searchValue = inputRef.current.value
navigate(`?term=${searchValue}`)
}
return (
<div>
<h1> Search </h1>
<form action="" onSubmit={formSubmitHandler}>
<input type="text" name="term" ref={inputRef} />
<input type="submit" value="Search" />
{/* Display the search term if it is present */}
{term && <h2>Results for '{term}'</h2>}
</form>
</div>
)
}
export default Search
page/UserDashboard.js
import React from 'react'
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
import "./Style.css";
const UserDashboard = () => {
let ids=1007;
return (
<div className='user__dashboard'>
<h1> User Dashboard </h1>
<Link to="profile" className='btn'> User Profile </Link>
<Link to={`/user/${ids}`} className='btn'> Edit Profile</Link>
</div>
)
}
export default UserDashboard
page/UserProfile.js
import React from 'react'
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom";
const UserProfile = () => {
const navigate = useNavigate();
return (
<div>
<h1> User Profile</h1>
<button onClick={() => navigate(-1)}>Go back</button>
</div>
)
}
export default UserProfile
page/UserEditProfile.js
import React from 'react'
import { useNavigate, useParams } from "react-router-dom";
import "./Style.css";
const UserEditProfile = () => {
let params = useParams();
let navigate = useNavigate();
const handleClick =()=> {
navigate('/user/profile');
};
return (
<div>
<h1> Edit Profile </h1>
<p> <b> Profile Id </b> : {params.editId} </p>
<button onClick={handleClick} className='btn__button'> useNavigate Instead of useHistory </button>
</div>
)
}
export default UserEditProfile